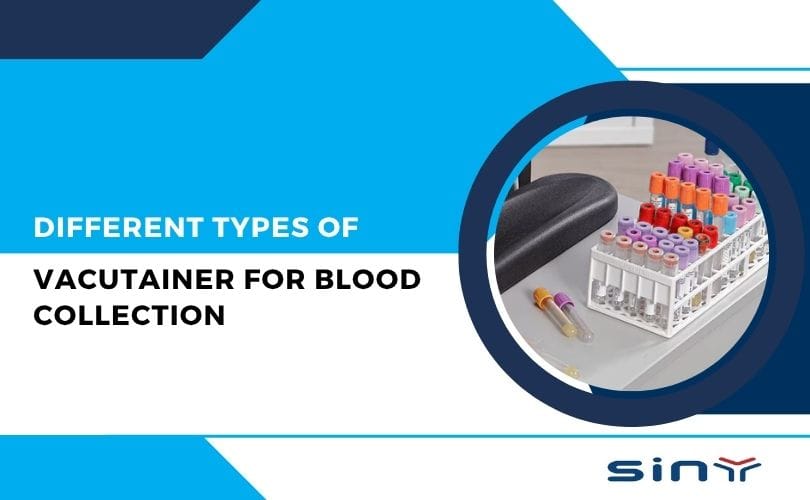
Blood collection is a critical process in diagnostic laboratories, hospitals, and research centers. One of the most widely used tools for blood sampling is the vacutainer for blood collection, a specialized vacuum tube designed to simplify and standardize blood collection while maintaining sample integrity. Selecting the appropriate vacutainer type is essential in ensuring accurate test results and patient safety. This detailed blog explores the different types of vacutainers, their components, applications, and advantages to provide medical professionals with expert knowledge to optimize their blood collection processes.
Table of Contents
What is a Vacutainer?
A Vacutainer is a blood collection device that uses a vacuum to draw blood into a tube. It consists of a needle, a holder, and a collection tube. The vacuum inside the tube collects the correct volume of blood, minimizing errors and contamination. Hospitals, clinics, and laboratories widely use Vacutainers because they offer convenience and reliability.
For more information on Vacutainers and their applications, visit Sinymedical.
Components of a Vacutainer
Understanding the components of a Vacutainer is essential for proper blood collection:
- Needle: Sterile and sharp, designed to penetrate the vein smoothly.
- Holder: Connects the needle to the tube and ensures stability during the procedure.
- Tube: Contains additives specific to the test requirements and maintains the vacuum.
For a detailed look at blood collection tubes, check out Blood Collection Tubes.
Why Are Vacutainers Important in Healthcare?
Blood testing is one of the most common and effective ways to monitor health conditions. But here’s the catch—using the wrong collection tube can alter results and lead to misdiagnosis.
For example:
- If an anticoagulant tube is used instead of a serum tube, blood won’t clot properly, affecting tests like liver function.
- Incorrect handling or choosing the wrong tube can lead to hemolysis (destruction of red blood cells), making the sample useless.
That’s why standardized vacutainer systems like those from SINY Medical ensure sample integrity from collection to analysis.
Types of Vacutainer Tubes for Blood Collection
Each vacutainer tube has a color-coded cap representing its additive and purpose. Let’s explore them in detail.
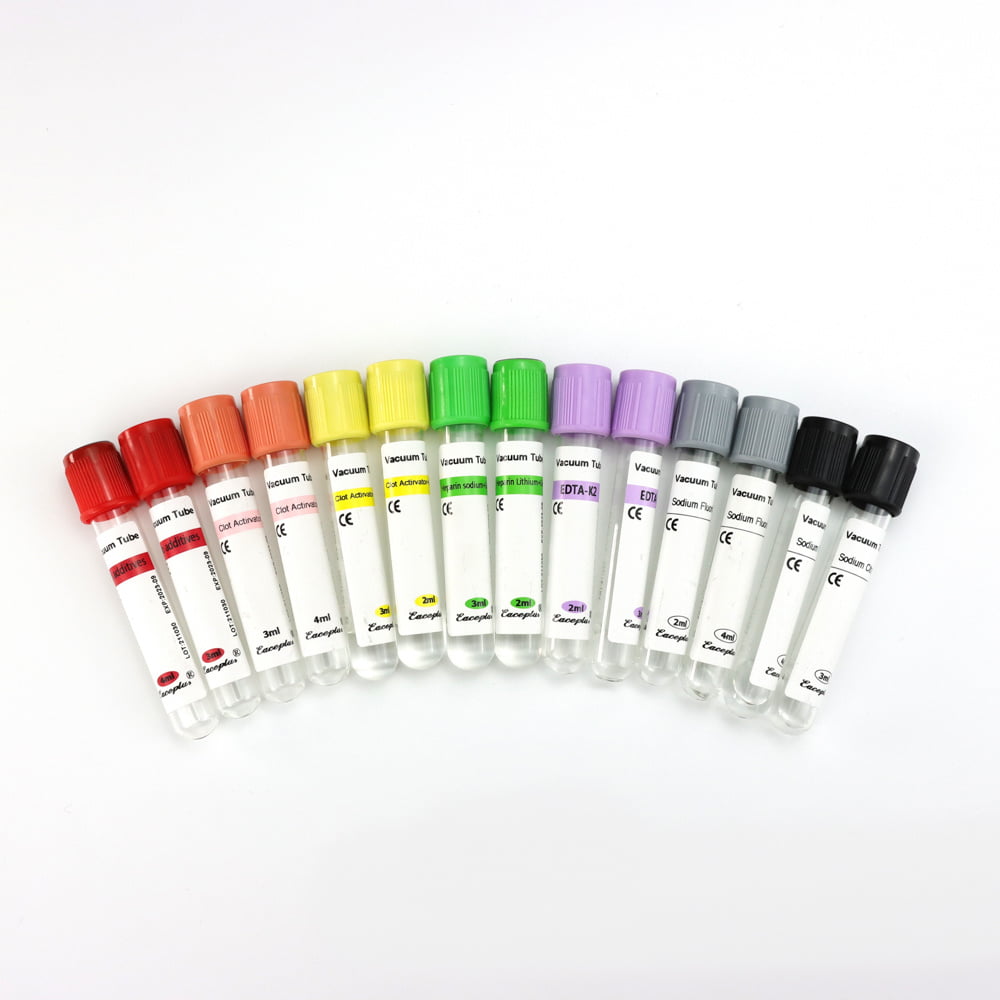

Serum Tubes (Red or Yellow Top)
- Additive: No anticoagulant; some may contain clot activators or gel separators
- Use: Serum chemistry, immunology, serology, and blood bank tests
- Clotting Time: 30 minutes before centrifugation
Serum tubes are commonly used for tests that require the liquid portion of blood without clotting factors. The gel separator helps in clean separation of serum for more accurate results.
👉 Check SINY Medical Serum Tube for detailed specifications.
EDTA Tubes (Purple or Lavender Top)
- Additive: Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA)
- Use: Hematology tests (CBC, blood films, HbA1c), molecular diagnostics
- Benefit: Prevents clotting by binding calcium ions
EDTA tubes are essential in blood cell studies because they preserve cellular structure better than other anticoagulants.
👉 Example: 2ml EDTA K2 Blood Collection Tube
👉 Non-vacuum option: EDTA Non-Vacuum Blood Collection Tube
Learn more about the differences in non-vacuum tubes.
Sodium Citrate Tubes (Light Blue Top)
- Additive: Sodium citrate solution (3.2% or 3.8%)
- Use: Coagulation studies like PT, aPTT, INR, D-dimer
- Function: Binds calcium to prevent clotting; easily reversible for coagulation testing
Citrate tubes are critical in monitoring blood clotting disorders and managing patients on anticoagulant therapy.
👉 Check 3ml Sodium Citrate Tube.
Heparin Tubes (Green Top)
- Additive: Lithium or sodium heparin
- Use: Plasma chemistry, electrolyte studies, and arterial blood gases
- Benefit: Provides plasma without clotting, faster turnaround compared to serum tubes
Heparin tubes are widely used in emergency settings where immediate results are required.
Fluoride Oxalate Tubes (Gray Top)
- Additive: Sodium fluoride and potassium oxalate
- Use: Glucose and lactate testing
- Function: Prevents glycolysis (breakdown of glucose in blood cells)
These are crucial for diabetes diagnosis and monitoring, ensuring sugar levels remain stable until analysis.
Plain Tubes (Red Cap, No Additive)
- Additive: None
- Use: Blood bank, drug level tests, serology
- Note: Require natural clotting before serum separation
Comparison Table of Vacutainer Tubes
| Tube Type | Cap Color | Additive | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serum Tube | Red/Yellow | Clot activator/gel | Chemistry, serology, immunology |
| EDTA Tube | Purple/Lavender | EDTA | Hematology, molecular tests |
| Sodium Citrate Tube | Light Blue | Sodium citrate | Coagulation studies |
| Heparin Tube | Green | Lithium/Sodium heparin | Plasma chemistry, ABG |
| Fluoride Oxalate Tube | Gray | Sodium fluoride + oxalate | Glucose, lactate tests |
| Plain Tube | Red (no additive) | None | Serology, drug tests |
Vacutainer Blood Collection Process
The process of drawing blood with a vacutainer is standardized to ensure sample accuracy:
- Prepare sterile equipment and select the appropriate tube.
- Apply a tourniquet and disinfect the puncture site.
- Insert needle and allow vacuum pressure to fill the tube.
- Invert the tube gently to mix additives.
- Label and send to the lab for analysis.
👉 For certified blood collection products, check SINY Medical Vacuum Blood Collection Vessel.
Why Choose Siny Medical for Your Vacutainers?
At Siny Medical, you can access superior quality vacutainer products that comply with stringent medical standards. Their range includes EDTA tubes, sodium citrate, serum tubes, and customized solutions with CE certification and bulk supply capabilities to meet the needs of clinics, hospitals, and laboratories globally. Detailed product information and purchasing options are available on their website.
Summary
Vacutainers revolutionize blood collection by providing safe, standardized, and efficient sampling tools ideal for diverse clinical applications. Knowing the different types of vacutainers—serum, EDTA, sodium citrate, heparin, and fluoride tubes—and selecting the right one according to test needs is crucial for diagnostic accuracy and patient care. Advanced technology and certified manufacturers like Siny Medical ensure medical professionals have access to trusted blood collection tubes that uphold the highest standards. For detailed product selections and consultations, visit their website or contact the Siny Medical team.
Expand your knowledge and product options with Siny Medical, and stay updated by watching their expert videos on YouTube or browsing their catalog on Made-in-China.
FAQs
What is the main difference between serum and plasma tubes?
Serum tubes allow blood to clot before centrifugation, yielding serum free of clotting factors. Plasma tubes contain anticoagulants, so plasma retains clotting proteins for tests like coagulation studies.
Why are vacutainers color-coded?
The color coding of stoppers helps quickly identify the kind of additive inside the tube, streamlining laboratory workflows and preventing errors.
Can vacutainers be reused?
No, vacutainers are single-use devices to prevent cross-contamination and ensure sterility.
What should be done if a vacutainer tube does not fill completely?
An incomplete fill may alter the blood-to-additive ratio, affecting test results. Such samples should be rejected or recollected.
How do I ensure proper vacuum in the tube?
Always check expiration date and tube integrity before use. Use compatible needles and collection techniques to maintain vacuum.
Where can I buy quality vacutainers?
Reliable sources like Siny Medical offer a comprehensive selection of quality vacutainers backed by certifications and customer support.