Medical testing relies heavily on the accuracy and reliability of blood sample collection. EDTA stands out for its unique properties and critical role among the various additives used in blood collection tubes.
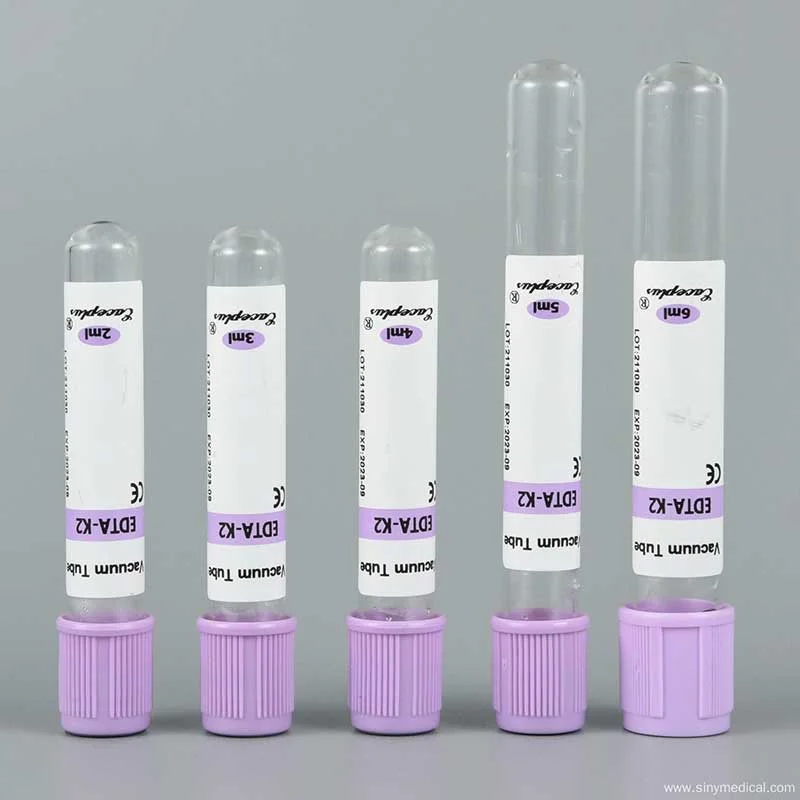
In medical laboratories, the integrity of blood samples is paramount. Ensuring that the blood remains in a suitable condition for analysis is crucial for obtaining accurate results. Blood sample collection tubes come with various additives designed to preserve the sample in specific ways. The purple top tubes, universally recognized in the medical community, contain EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) as their additive.
Table of Contents
- 1 Understanding EDTA
- 2 The Role of EDTA in Blood Collection
- 3 What is Purple Top Tubes?
- 4 Why Purple Top Tubes?
- 5 How EDTA prevents blood clotting in purple top tubes
- 6 Benefits of EDTA in Purple Top Tubes
- 7 The importance of using EDTA in blood collection and storage
- 8 EDTA vs. Other Anticoagulants
- 9 Final Thoughts
- 10 FAQs
Understanding EDTA
What is EDTA?
EDTA, or Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, is a chelating agent that binds to metal ions. It was first synthesized in the 1930s and has since found widespread use in various industries, including medicine, food processing, and cleaning products. In the medical field, its primary role is as an anticoagulant in blood collection tubes.

Chemical Properties of EDTA
EDTA is a molecule composed of four carboxyl groups and two amine groups. Its structure allows it to bind tightly to divalent metal ions such as calcium and magnesium. This binding capability gives EDTA Tubes, it anticoagulant properties, as calcium ions are essential for blood clotting. By sequestering these ions, EDTA effectively prevents the coagulation cascade, maintaining the blood in a fluid state suitable for analysis.
The Role of EDTA in Blood Collection
Anticoagulant Properties
The primary reason for using EDTA in purple top tubes is its powerful anticoagulant properties. When blood is collected, the natural clotting process begins immediately. Without an anticoagulant, the blood sample would coagulate, rendering it unusable for many analyses. By binding to calcium ions, EDTA inhibits the clotting process, preserving the sample in a liquid state.
Preventing Coagulation
Blood coagulation involves a complex cascade of reactions, with calcium ions playing a pivotal role. EDTA cheats these ions, effectively removing them from the reaction pathway. This action prevents the formation of fibrin clots, ensuring that the blood remains fluid and easy to work with for laboratory tests.
EDTA’s Interaction with Calcium
Calcium ions are necessary for the activation of clotting factors in the blood. EDTA’s ability to bind these ions means it can effectively halt coagulation. This rapid and stable interaction makes EDTA an ideal choice for preserving blood samples for extended periods.
What is Purple Top Tubes?
Purple top tubes are blood collection tubes that contain EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) as an anticoagulant. They are primarily used in hematology tests, such as complete blood counts (CBC), due to their ability to preserve the shape and size of blood cells and prevent clotting. The distinctive purple cap ensures quick identification, standardizing the blood collection process in medical laboratories and ensuring the accuracy of diagnostic results.
Why Purple Top Tubes?
Color-Coding in Blood Collection
Color-coded tubes streamline blood collection in clinical settings and ensure the correct additives are used for specific tests. The purple top tube, universally associated with EDTA, allows healthcare professionals to quickly and reliably identify the correct tube for complete blood counts (CBC) and other hematology tests
Standardization in Medical Testing
Standardization is critical in medical testing to ensure consistency and reliability of results. The use of purple top tubes for EDTA-containing samples is a widely accepted standard. This consistency helps to avoid confusion and errors in the blood collection process, contributing to the overall accuracy of diagnostic tests.
How EDTA prevents blood clotting in purple top tubes
The mechanism by which EDTA prevents blood clotting in purple top tubes is a fascinating example of the intricate interplay between chemistry and biology. When blood is drawn into a purple top tube, the EDTA immediately begins binding to the calcium ions in the sample.

Calcium ions play a critical role in coagulation, serving as cofactors for various enzymes involved in the clotting cascade. By sequestering these calcium ions, EDTA effectively disrupts the normal functioning of the clotting system, preventing the formation of fibrin. This insoluble protein forms the backbone of a blood clot.
EDTA does not absolutely prevent blood clotting; it simply delays the coagulation process, providing a window of time during which you can process and analyze the blood sample. This window can vary depending on factors such as the concentration of EDTA in the tube, the volume of the blood sample, and the storage conditions.
Benefits of EDTA in Purple Top Tubes
Preserving Blood Cell Integrity
One of the critical benefits of EDTA is its ability to preserve the integrity of blood cells. Unlike some other anticoagulants, EDTA does not cause significant alterations to the morphology of blood cells. This preservation is crucial for accurate cell counts and morphological assessments.
Minimal Interference with Cell Analysis
EDTA is known for its minimal interference with various analytical processes. Its presence does not significantly affect the measurement of most analytes, making it suitable for a wide range of tests. This characteristic is essential in hematology, where precise cell counts and differentials are necessary.
Stability of Blood Samples
Blood samples treated with EDTA remain stable for extended periods, allowing for more flexible handling and processing times. This stability proves especially beneficial when immediate analysis is impossible, such as when transporting samples to a different location for testing.
The importance of using EDTA in blood collection and storage
The use of EDTA in blood collection, particularly in purple top tubes, is fundamental for ensuring the precision and dependability of medical diagnostic tests. This chemical serves a vital function beyond mere convenience, pivotal in the accuracy of crucial hematological measurements.
Critical for Hematological Accuracy
EDTA prevents the clotting of blood, which is essential for accurately measuring various blood components such as red and white blood cells, hemoglobin levels, and platelet counts. These parameters are crucial for diagnosing and monitoring multiple health conditions, including anemia, leukemia, infectious diseases, and chronic illnesses. Without EDTA, blood samples would coagulate rapidly, potentially leading to unreliable results and, worse, misdiagnosis or delayed treatment.
Beyond Hematology
The benefits of EDTA blood collection tubes extend to biochemical analyses as well. Tests that measure electrolyte levels, liver function, kidney function, and more depend on EDTA’s stability in blood samples. EDTA prevents enzymatic activity that could alter the sample during storage or transport by chelating calcium ions and other divalent metal ions necessary for enzyme-driven reactions.
Essential During Sample Transport
EDTA stabilizes blood samples, which is especially crucial during transportation to centralized laboratories. It preserves the biological characteristics of the sample, maintaining its original state despite potential variations in transit conditions. This stabilization allows healthcare providers to rely on the results to make informed decisions regarding patient care and treatment plans.
EDTA in blood collection tubes is indispensable for maintaining the integrity and stability of blood samples, enabling the accurate and reliable results necessary for effective medical diagnosis and management.
EDTA vs. Other Anticoagulants
While EDTA is widely used, it is not the only anticoagulant available. Understanding its advantages over other options can highlight why it is preferred for specific applications.
Citrate
Citrate is another commonly used anticoagulant, particularly in coagulation studies. EDTA, citrate works by binding calcium ions reversibly. This reversibility is crucial for coagulation tests, where the ability to reintroduce calcium is necessary for specific assays.
Heparin
Heparin is an anticoagulant that works by inhibiting thrombin and other clotting factors. It is often used in clinical chemistry tests where plasma is required. However, heparin can interfere with some assays and cause cellular changes, making it less suitable for hematology tests than EDTA.
Final Thoughts
The use of EDTA in purple top tubes is a cornerstone of modern medical diagnostics. Its powerful anticoagulant properties, ability to preserve blood cell integrity, and minimal interference with analytical processes make it the additive of choice for many blood tests. Understanding the importance of EDTA and the reasons behind its widespread use can help ensure the accuracy and reliability of blood test results.
FAQs
What are purple top tubes used for?
Medical professionals primarily use purple top tubes for hematology tests, including complete blood counts (CBC) and other tests that require preserved blood cells
How does EDTA prevent blood coagulation?
EDTA prevents blood coagulation by chelating calcium ions, essential for clotting. This action inhibits the formation of clots, keeping the blood in a fluid state suitable for analysis.
Are there alternatives to EDTA for blood collection?
Yes, there are alternatives to EDTA tubes, such as citrate and heparin. Each has specific uses and advantages, depending on the type of test conducted. However, medical professionals often prefer EDTA for hematology tests due to its superior ability to preserve cell morphology and its minimal interference with various assays
How should purple top tubes be stored?
Store purple top tubes at room temperature, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. This proper storage maintains the EDTA’s stability and preserves the integrity of the blood samples once collected.
Can EDTA interfere with test results?
EDTA minimizes interference with most tests, but it can affect specific assays sensitive to chelating agents. Therefore, use the appropriate type of collection tube based on the specific requirements of the test being conducted.
Why is the color purple used for these tubes?
These tubes use purple as part of a standardized color-coding system in medical laboratories. This system helps healthcare professionals quickly identify the type of additive in the tube and ensures they use the correct tube for the appropriate test.