Blood collection is a fundamental procedure in medical diagnostics, and the tools utilized for this process significantly impact the patient experience and the quality of the samples obtained. Among the various methods available, the needle with Vacutainer system from Sinymedical has become a standard in many healthcare settings. This article explores the pros and cons of using a needle with a Vacutainer, providing a comprehensive overview for healthcare professionals and patients.
Table of Contents
The needle with Vacutainer system is a blood collection device that combines a hollow needle with a vacuum-sealed tube. This system allows for efficient and safe collection of blood samples, minimizing contamination and maintaining sample integrity. Developed in the 1940s, the Vacutainer system revolutionized phlebotomy by providing a closed, sterile environment for blood collection.
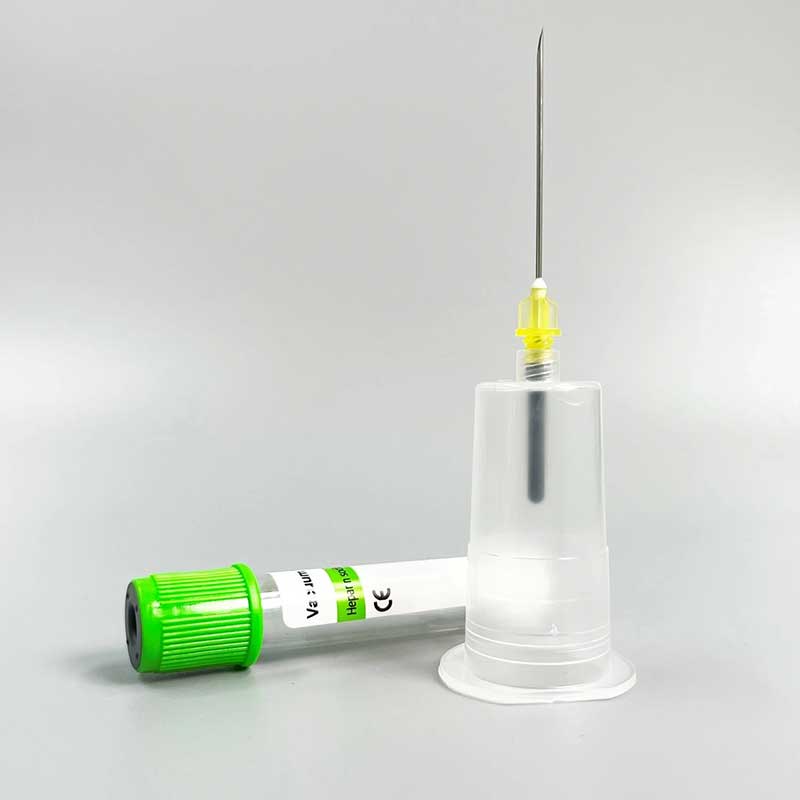
The Needle with Vacutainer system, consisting of a double-ended needle, a plastic holder, and vacuum-sealed tubes, offers a standardized method for blood collection. Its widespread use in hospitals, clinics, and laboratories underscores its significance in medicine. However, like any medical device, it has advantages and disadvantages.
Safety and Efficiency
The Needle with Vacutainer system is designed to enhance safety and efficiency in blood collection. The vacuum-sealed tubes reduce the risk of contamination and ensure a clean and precise draw. The system’s design minimizes the risk of accidental needle sticks, which is a significant concern for healthcare workers.
One of the most notable benefits of the Needle with Vacutainer is the reduction in needlestick injuries. The device’s design ensures the needle is securely covered before and after use, protecting healthcare workers from accidental punctures and potential exposure to bloodborne pathogens.
The standardization provided by the Needle with Vacutainer system is invaluable. It ensures consistent sample quality and volume, crucial for accurate diagnostic testing. This uniformity helps in reducing variability in test results, leading to more reliable and comparable data.
Patient comfort is a critical aspect of blood collection. The Needle with Vacutainer system is designed to minimize discomfort during the procedure. The quick and efficient draw reduces the time the needle is in the vein, making the experience less distressing for patients.
The quality of blood samples collected using the Needle with Vacutainer is generally high. The vacuum-sealed tubes prevent air from entering, which can lead to hemolysis or clotting. This preservation of sample integrity is essential for accurate laboratory analysis.
While the initial investment in Needle with Vacutainer systems may be higher, they are cost-effective in the long run. Reducing needlestick injuries and standardizing samples lead to fewer errors and retests, saving time and resources.
The Needle with Vacutainer system is user-friendly and requires minimal training for healthcare professionals. Its straightforward design allows for quick and efficient blood collection, which is particularly beneficial in high-volume settings such as hospitals and clinics.
The initial cost of implementing the Needle with Vacutainer system can be a barrier for some healthcare facilities. While it is cost-effective over time, the upfront investment in equipment and training can be significant.
Proper use of the Needle with Vacutainer system requires training. Healthcare workers must be educated on the correct techniques to avoid complications such as improper draws or hemolysis. This training can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Although the Needle with Vacutainer system is designed to minimize hemolysis, it can still occur if the technique is not correctly executed. Factors such as excessive force during blood draw or improper handling of tubes can lead to sample degradation.
The disposal of the Needle with Vacutainer components raises environmental concerns. The plastic and needle components must be disposed of properly to avoid pollution and potential harm to wildlife. This requires effective waste management systems, which can be challenging to implement.
In certain complex cases, such as patients with difficult venous access, the Needle with Vacutainer system may not be the best option. Alternative methods, such as butterfly needles or capillary collection, may be required to obtain a viable sample.

Clinical Use
The Needle with Vacutainer system is extensively used in clinical settings for routine blood draws, diagnostic testing, and monitoring of chronic conditions. Its reliability and efficiency make it a preferred choice for healthcare professionals.
Research Applications
In research settings, the Needle with Vacutainer system is invaluable for collecting blood samples for various studies. The standardized sample quality ensures consistency in research data, which is crucial for the validity of experimental results.
Home Use and Self-Collection
With technological advancements, the Needle with Vacutainer system is now being adapted for home use and self-collection. This is particularly beneficial for patients requiring frequent blood tests, such as those with diabetes or on anticoagulant therapy.
Syringes and Needles
Traditional syringes and needles are still used in many settings. However, they come with a higher risk of needlestick injuries and require more skill to use effectively. The Needle with Vacutainer system offers a safer and more standardized alternative.
Butterfly Needles
Butterfly needles are often used for patients with minor or fragile veins. While they offer greater flexibility in complex cases, they are generally more expensive and less standardized than the Needle with Vacutainer system.
Capillary Collection
Capillary blood collection is typically performed using a lancet, which is used for specific tests such as glucose monitoring. While it is less invasive, it is unsuitable for all types of blood tests and may need to provide sufficient sample volume for comprehensive analysis.
Conclusion
The Needle with Vacutainer system offers numerous advantages, including enhanced safety, efficiency, and standardization in blood collection needle. However, it also comes with challenges like initial cost, training requirements, and environmental concerns. Understanding these pros and cons is essential for healthcare professionals, patients, and researchers to make informed decisions about blood collection methods.
A Needle with Vacutainer is a medical device used to collect blood samples. It comprises a double-ended needle, a plastic holder, and vacuum-sealed tubes. This system facilitates efficient and safe blood draws, minimizing the risk of contamination and needlestick injuries.
The Needle with Vacutainer creates a vacuum inside the collection tube, which draws blood from the patient’s vein into the tube. Insert the double-ended needle into the vein, and push the vacuum-sealed tube onto the needle inside the holder. The vacuum maintains a steady flow as the tube fills with blood until collecting the desired amount.
The Needle with Vacutainer offers several benefits, including increased safety due to reduced needlestick injuries, standardized blood collection processes, and improved patient comfort. Additionally, it ensures high sample quality and is cost-effective over time due to fewer errors and retests. The system is also user-friendly, requiring minimal training for healthcare professionals.
While the Needle with Vacutainer system is highly beneficial, it has some drawbacks. These include the initial cost of equipment and training, the potential for hemolysis if not used correctly, and environmental concerns related to the disposal of plastic components. Additionally, the system may not be suitable for patients with difficult venous access.
Proper disposal of Needle with Vacutainer components is crucial for environmental and safety reasons. Dispose of used needles in designated sharps containers to prevent injury and contamination. Recycle plastic components when possible, but always follow local regulations for medical waste disposal to minimize environmental impact.
Recent innovations in Needle with Vacutainer technology include automated blood draw devices and smart vacutainers that can communicate with laboratory systems for improved efficiency and accuracy.