Syringes and needles are two of the most commonly used instruments.They are often mentioned together, they serve distinct purposes and have unique features. Understanding the differences between a syringe and a needle is crucial for medical professionals, patients, and anyone involved in healthcare. This blog will delve into the real differences between syringes and needles, their uses, types, and how they work together to deliver effective medical care. A healthcare provider or simply curious, this guide will provide you with comprehensive insights.
Table of Contents
- 1 What is a Syringe?
- 2 What is a Needle?
- 3 Syringe vs Needle: What’s the Real Difference?
- 4 Key Differences Between Syringe vs Needle
- 5 How Syringes and Needles Work Together
- 6 Types of Syringes & Needles
- 7 Different Types of Medical Needles Explained
- 8 Standard Hypodermic Needles
- 9 Butterfly Needles
- 10 Blood Collection Needles
- 11 Safety Needles
- 12 Safety Features: Syringe vs Needle
- 13 Choose a Syringe
- 14 Summary
- 15 FAQs
What is a Syringe?
A syringe is a medical device used to inject or withdraw fluids from the body. It consists of a barrel, a plunger, and a tip where the needle is attached. Syringes come in various sizes and types, each designed for specific medical applications. A syringe holds and dispenses liquids, consisting of a barrel, a plunger, and a tip where the needle attaches.
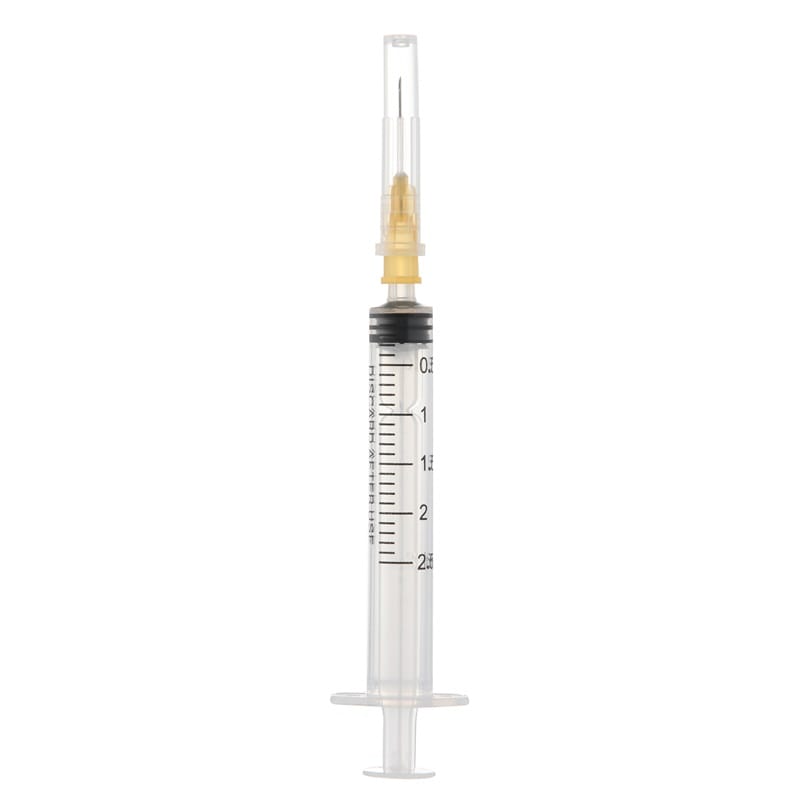
Key Features of a Syringe:
- Barrel: The cylindrical part that holds the liquid.
- Plunger: The movable part that pushes or pulls the liquid.
- Tip: The end where the needle is attached.
Syringes are essential tools in vaccinations, medication administration, and fluid extraction. For more information on different types of syringes, visit our Syringe Products page.
What is a Needle?
A needle is a thin, hollow tube with a sharp tip designed to penetrate the skin or other tissues. Needles are attached to syringes to deliver medications, draw blood, or perform other medical procedures. They come in various gauges (thickness) and lengths, depending on their intended use. Butterfly needles serve blood collection purposes, and safety injection needles minimize the risk of needlestick injuries.
Key Features of a Needle
- Gauge: The thickness of the needle (lower gauge = thicker needle).
- Length: The size of the needle, which varies based on the application.
- Bevel: The slanted tip that allows for smooth penetration.
Needles are critical in procedures like blood collection, IV therapy, and vaccinations, and Blood Collection Needle and Butterfly Needle.
Syringe vs Needle: What’s the Real Difference?
A syringe and a needle work hand-in-hand, their roles are completely different:
- A syringe holds and controls the medication or fluid.
- A needle punctures the skin and delivers (or removes) the fluid.
Think of the syringe as the “engine” and the needle as the “delivery tool.” Without one, the other is almost useless.
To make the differences clearer, let’s explore them one by one.
Key Differences Between Syringe vs Needle
Below is a clear, research-backed comparison table to settle the confusion.
| Feature | Syringe | Needle |
|---|---|---|
| Main Purpose | Holds and pushes fluid | Pierces skin/tissue |
| Material | Plastic barrel + rubber plunger | Stainless steel |
| Reusable? | Usually single-use | Always single-use |
| Measurement Markings | Yes | No |
| Connection | Luer-slip, Luer-lock, fixed | Hub connects to syringe |
| Risk Factor | Low | Needle-stick injuries |
| Used For | Injecting or extracting fluids | Delivering or withdrawing through skin |
How Syringes and Needles Work Together
Syringes and needles are often used in tandem to perform medical procedures. The syringe holds the medication or fluid, the needle delivers or extracts it from the body. A vaccination, the syringe is filled with the vaccine, and the needle is used to inject it into the patient’s muscle or skin. In blood collection, the needle is inserted into the vein, and the syringe is used to draw blood.
Types of Syringes & Needles
Type of Syringes
- Disposable Syringes: Single-use syringes to prevent contamination. Learn more about our Disposable Self-Destructive Retractable Syringe with Needle.
- Insulin Syringes: Designed for diabetic patients to administer insulin.
- Luer Lock Syringes: Feature a locking mechanism to securely attach the needle.
Type of Needles
- Butterfly Needles: Ideal for blood collection in patients with small or fragile veins.
- Safety Needles: Designed to reduce the risk of needlestick injuries.
- Hypodermic Needles: Used for injections under the skin or into muscles.
Different Types of Medical Needles Explained
Certain procedures require special needle designs.
Standard Hypodermic Needles
Used for most injections.
Gauge varies from 18G (thick) to 30G (ultra-thin).
Butterfly Needles
These needles have flexible wings on both sides for extra control.
They’re used mainly for:
- Drawing blood
- Difficult veins
- Pediatric patients
Explore:
👉 Butterfly Needle from Siny Medical.
Blood Collection Needles
Designed for multi-sample blood draws using vacuum tubes.
Check here:
👉 Blood Collection Needles.
Safety Needles
These include special shields or retractable features to avoid accidental needle sticks—one of the top occupational hazards for nurses.
See the full lineup:
👉 Safety Injection Needles.
Safety Features: Syringe vs Needle
Safety is a huge part of modern injection systems.
Here’s what matters most:
Syringe Safety Features
- Retractable mechanism
- One-way plunger lock
- Sterile packaging
- Leak-proof barrel
Needle Safety Features
- Needle shields
- Automatic retraction
- Anti-stick coverings
- Protective wing designs
Siny Medical manufactures a variety of these advanced safety products at international quality standards:
👉 https://sinymedical.en.made-in-china.com/
👉 www.youtube.com/@sinymedical
Choose a Syringe
The decision depends on:
- Type of medication
- Patient age
- Viscosity of liquid
- Depth of injection
- Procedure purpose
Example:
- Thick medications need a lower gauge (bigger) needle.
- Insulin needs a fine, fixed-needle syringe.
- Blood draws require butterfly or blood collection needles.
Which syringe or needle is best for your clinic, you can always contact Siny Medical for expert guidance:
👉 Contact Siny Medical.
Summary
Syringes and needles are essential medical tools with distinct roles. A syringe is used to hold and dispense liquids, a needle is designed to penetrate tissues for injection or extraction. Understanding their differences and applications is crucial for safe and effective medical care. You’re administering a vaccine, drawing blood, or delivering medication, choosing the right syringe and needle is key. For high-quality medical supplies, explore our range of products at Siny Medical.
For more insights, check out our YouTube Channel and Made-in-China Profile. Any questions, feel free to Contact Us.
FAQs
1. Can I reuse a syringe or needle?
No, reusing syringes or needles can lead to infections and contamination. Always use disposable syringes and needles for single-use purposes.
2. What is the difference between a syringe and a needle?
A syringe is used to hold and dispense liquids, a needle is used to penetrate tissues for injection or extraction.
3. How do I choose the right syringe and needle?
The choice depends on the procedure. Use an insulin syringe for diabetes management or a butterfly needle for blood collection.