In clinical laboratories, accurate blood sample collection is crucial for reliable test results. The correct anticoagulant tube can significantly impact diagnostic outcomes. Two of the most commonly used anticoagulant tubes are the Sodium Citrate Tube and the EDTA Tube. Understanding the differences between these tubes helps healthcare professionals and laboratory technicians select the optimal tube for various tests and avoid sample errors.
The Siny Medical brand is known globally for producing top-quality medical and laboratory supplies, including EDTA Tubes and ESR Tubes. Their precision manufacturing ensures consistent performance and reliability in clinical environments.
Table of Contents
- 1 What is a Sodium Citrate Tube?
- 2 What is an EDTA Tube?
- 3 Comparison of Sodium Citrate Tube vs EDTA Tube
- 4 Applications of Sodium Citrate Tubes and EDTA Tubes
- 5 Clinical Tests Using Sodium Citrate and EDTA Tubes
- 6 Which Tube Should You Choose?
- 7 Why Proper Tube Selection Matters
- 8 Manufacturing Excellence: Siny Medical’s Role
- 9 Color Coding and Identification
- 10 Summary
- 11 FAQs
What is a Sodium Citrate Tube?
A Sodium Citrate Tube contains sodium citrate as its anticoagulant. This additive works by binding calcium ions in the blood, effectively preventing clot formation.

These tubes are typically recognized by their light blue caps and are primarily used in coagulation studies, such as PT (Prothrombin Time) and APTT (Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time).
Chemical Mechanism
Sodium citrate binds calcium ions in blood plasma, preventing coagulation. This process is reversible — when calcium is reintroduced during testing, normal clotting can occur, allowing for accurate assessment of coagulation factors.
Features of Sodium Citrate Tubes:
- Usually contain 3.2% or 3.8% sodium citrate solution
- Maintain the integrity of clotting factors
- Used for coagulation studies and ESR tests
- Require a precise blood-to-additive ratio (typically 9:1)
For reliable and certified options, explore Siny Medical’s 4ml 3.8% Sodium Citrate Tube for standardized sample collection.
What is an EDTA Tube?
An EDTA Tube contains Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) as its anticoagulant. It works by chelating calcium ions, permanently removing them from the blood and preventing clot formation.
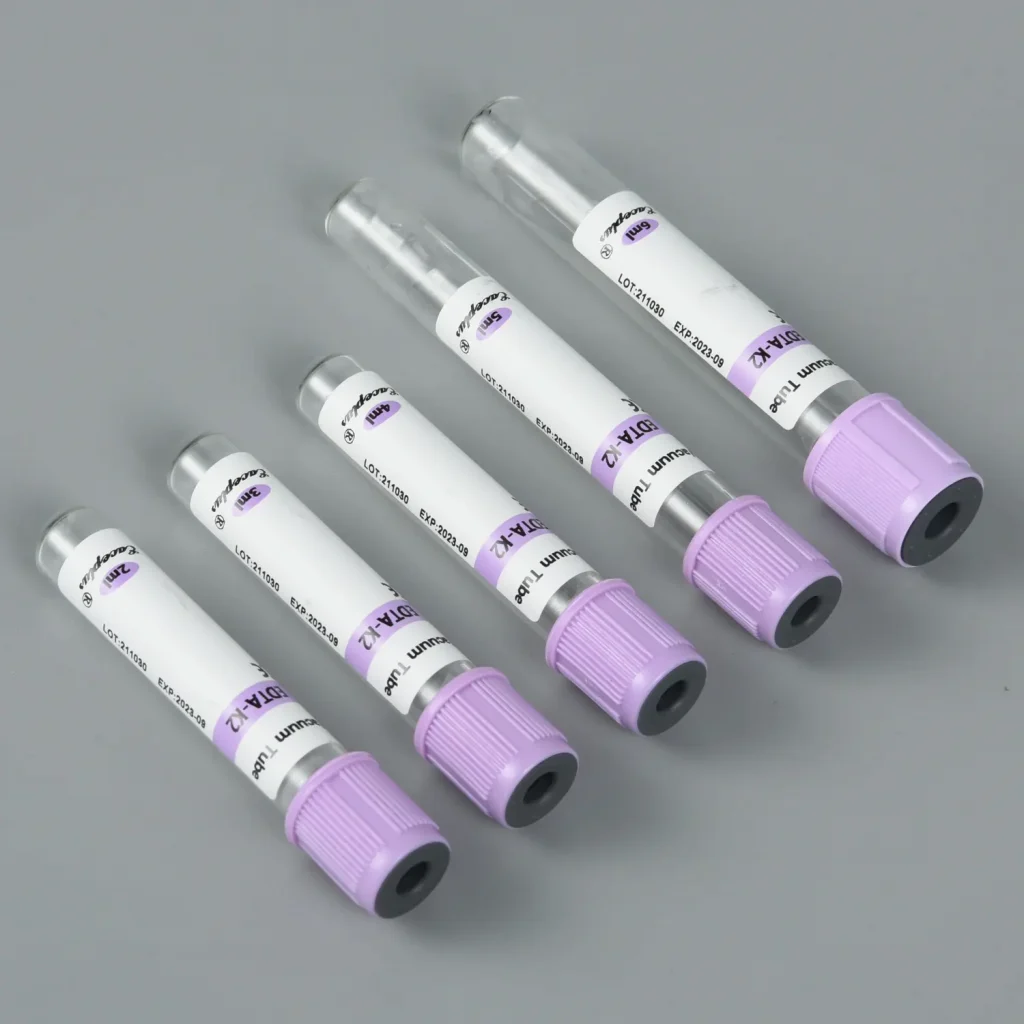

The EDTA Tube stands out with its lavender or purple cap, making it easily identifiable. Laboratories widely use it for hematology tests, including Complete Blood Count (CBC), hemoglobin analysis, and platelet counts.
Chemical Mechanism
EDTA binds calcium strongly and irreversibly, meaning that once chelated, calcium cannot be reintroduced to restore clotting. This ensures a stable cellular environment ideal for analyzing blood cells.
Features of EDTA Tubes
- Contains K2 or K3 EDTA
- Provides excellent preservation of cellular morphology
- Used for CBC, WBC count, and ESR (in some cases)
- Prevents platelet aggregation and hemolysis
You can explore EDTA Tubes for Blood Collection from Siny Medical for high-quality, sterile sample collection solutions.
Comparison of Sodium Citrate Tube vs EDTA Tube
| Feature | Sodium Citrate Tube | EDTA Tube |
|---|---|---|
| Anticoagulant | Sodium Citrate | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) |
| Mode of Action | Binds calcium reversibly, prevents clotting during coagulation tests | Binds calcium irreversibly, prevents clotting in hematological tests |
| Color Coding | Light blue cap | Lavender or purple cap |
| Clinical Uses | Coagulation tests (PT, aPTT, ESR) | Hematology tests (CBC), blood typing |
| Specimen Viability Time | Stable up to 4 hours at room temperature | Stable up to 24 hours or more if stored appropriately |
| Sample Volume Ratio | Exact fill ratio of blood to anticoagulant (9:1) critical | Flexible fill volume |
| Handling Requirement | Must be gently inverted 3–4 times immediately after collection | Invert 8–10 times immediately to mix anticoagulant |
| Impact on Test Results | Overfilling or underfilling can skew coagulation results | Excess EDTA can cause artifact effects like platelet clumping |
Applications of Sodium Citrate Tubes and EDTA Tubes
Sodium Citrate Tube Applications:
- Coagulation Testing: Essential for evaluating clotting factors, PT, and APTT.
- ESR Testing: Used with ESR Tubes that utilize sodium citrate to determine inflammation.
- Platelet Function Tests: Maintains accurate platelet function due to minimal interference.
Learn more about How ESR Tube Anticoagulants Work to understand sodium citrate’s role in preventing false test results.
EDTA Tube Applications
- Hematology: Used in CBCs, blood smears, and differential leukocyte counts.
- Blood Banking: Ideal for cross-matching and blood typing.
- Molecular Biology: Prevents nucleic acid degradation, preserving DNA and RNA integrity.
Siny Medical provides precision EDTA Tubes suitable for both manual and automated analyzers.
Clinical Tests Using Sodium Citrate and EDTA Tubes
The choice of tube depends on the laboratory test’s requirements:
- Tests for Sodium Citrate Tubes:
Prothrombin Time (PT)
Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT)
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
Coagulation factor assays - Tests for EDTA Tubes:
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
White Blood Cell (WBC) differential
Hemoglobin and hematocrit tests
Molecular and genetic testing
Detailed product categories with specifications for Sodium Citrate and EDTA tubes are available here:
Siny Medical ESR Tube Product Category
Which Tube Should You Choose?
Choosing the right tube depends entirely on the type of test being performed:
- For Coagulation Tests: Always use Sodium Citrate Tubes.
- For Hematology Tests: Use EDTA Tubes.
- For ESR Tests: Prefer Sodium Citrate, but EDTA can be used when necessary.
Using the wrong tube could result in erroneous lab values, clotted samples, or inaccurate reports — issues that can have serious diagnostic consequences.
Why Proper Tube Selection Matters
Selecting the correct tube ensures:
- Accurate Test Results
- Prevention of Clotting or Hemolysis
- Reproducibility in Clinical Trials
- Longer Sample Stability
- Reliable Diagnostic Outcomes
To guarantee top-tier accuracy, laboratories rely on high-quality, sterile tubes such as those manufactured by Siny Medical.
Manufacturing Excellence: Siny Medical’s Role
Siny Medical is one of the 10 Leading ESR Tube Manufacturers with a global reputation for precision and quality.
They offer a range of certified medical devices, including:
For more insights into their product line, visit their YouTube Channel and Made-in-China Page.
Color Coding and Identification
Each tube’s cap color follows international standards:
- Light Blue: Sodium Citrate (used for coagulation)
- Lavender/Purple: EDTA (used for hematology)
- Black or Red: Varies by additive type
You can learn more about What Is the ESR Tube Color? from Siny Medical’s educational resource.
Summary
Understanding the differences between Sodium Citrate Tubes and EDTA Tubes is essential in clinical laboratory diagnostics. Sodium Citrate Tubes specialize in coagulation testing due to their reversible calcium-binding properties and strict volume ratio requirements. EDTA Tubes preserve blood cell morphology, making them ideal for hematology and molecular assays. Proper tube selection, meticulous handling, and knowledge of their specific applications ensure accurate test results and effective patient care.
Partner with trusted suppliers like Siny Medical to access quality anticoagulant tubes designed for reliability and precision in medical laboratories.
FAQs
Q1: Can Sodium Citrate Tubes be used for CBC tests?
No, Sodium Citrate Tubes are not suitable for hematology tests like CBC because they alter cellular morphology, unlike EDTA Tubes, which preserve cells effectively.
Q2: How critical is the fill volume for Sodium Citrate Tubes?
Extremely critical. The blood to anticoagulant ratio must be precise (usually 9:1). Underfilled or overfilled tubes lead to inaccurate coagulation test results.
Q3: How long can blood samples in EDTA Tubes be stored before analysis?
EDTA blood samples are stable for 24 hours at room temperature and longer if refrigerated, making them more flexible for hematology testing.
Q4: What happens if EDTA Tubes are used for coagulation tests?
Using EDTA tubes for coagulation tests can cause false results since EDTA irreversibly binds calcium and disrupts coagulation pathways.
Q5: Where can I purchase high-quality Sodium Citrate and EDTA Tubes?
You can find a range of tubes with certification and quality assurance at Siny Medical, including detailed product specs for Sodium Citrate Tubes and EDTA Tubes.