Drawing blood safely and efficiently plays a vital role in clinical diagnostics. The Vacutainer® system, paired with the right blood collection needle, streamlines sample handling for lab tests. Here, we compare two common needles—winged “butterfly” needles and straight needles—in terms of design, performance, sample quality, clinical use, and best practices. This guide helps lab staff choose the right tool to ensure patient comfort, reliable results, and smooth workflows.
Table of Contents
What is a Butterfly needle?
The butterfly needle ranges in size from 18 to 23 and has a thinner gauge. A higher gauge number indicates a thinner diameter, making butterfly needles one of the thinnest needles used by sinymedical.

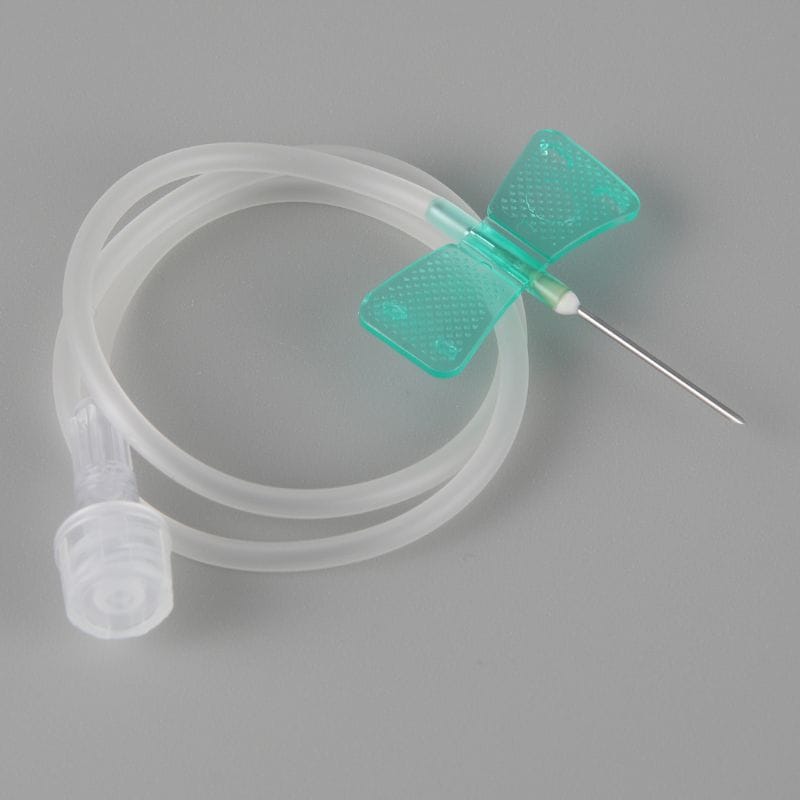
A Butterfly Needle, also called a winged infusion set, is a small, thin needle attached to two flexible “wings” and a short length of tubing. It’s most commonly used for venipuncture (drawing blood), IV infusions, or for patients with small, fragile, or difficult-to-locate veins—think children, elderly patients, or people undergoing chemotherapy.
What Is a Regular Needle?
A Butterfly Needle, also called a winged infusion set, is a small, thin needle attached to two flexible “wings” and a short length of tubing. It’s most commonly used for venipuncture (drawing blood), IV infusions, or for patients with small, fragile, or difficult-to-locate veins—think children, elderly patients, or people undergoing chemotherapy.
Design and Materials
Needle Size and Shape
1. Butterfly Needle
- Flexible tubing made of polyurethane or medical-grade siliconeWinged tabs on each side for easy grip and secure holdTip size: 23G (0.6 mm), 22G (0.7 mm), or 21G (0.8 mm).
- Tip size: 23G (0.6 mm), 22G (0.7 mm), or 21G (0.8 mm)
2. Straight Needle
- Tip size: 21G (0.8 mm), 22G (0.7 mm), 23G (0.6 mm); other gauges like 20G or 24G also exist
- Rigid stainless-steel shaft with a polypropylene hub
- No tubing or wings; shaft length around 38–45 mm
Tube Connection
- Butterfly needles use a Luer Lock or Luer Slip adapter that fits most Vacutainer tubes.
- Straight needles click directly into the tube holder, making setup quick and secure.
Sterility and Safety
- Both needle types arrive sterile, using gamma radiation or ethylene oxide per ISO 11137 and ISO 11135.
- Use each device once, then discard it in a sharps container according to local medical waste rules.
Flow Dynamics and Sample Quality
Vacuum Pressure and Flow Rate
Vacutainer® tubes hold a vacuum of about –0.3 to –0.6 bar. This pull draws blood into the tube. Matching needle gauge and tube vacuum prevents:
- Turbulence, which can damage blood cells, and
- Vein collapse, which stops the draw prematurely.
Hemolysis and Clotting
Butterfly Needle
- Gentle flow through flexible tubing cuts turbulence and keeps hemolysis under 0.5%.A stable position reduces the need for repeat sticks.
- A stable position reduces the need for repeat sticks.
Straight Needle
Faster draw fits high-volume tests (chemistry panels, hormones) but risks up to 1.0% hemolysis if too forceful.
Additives and Coatings
- Common tubes use EDTA (for blood counts), heparin (for blood gases), citrate (for clotting tests), or clot activator (for serum).
- Some tubes carry separation gel or powdered clot activator to speed serum or plasma separation and extend sample stability for up to five days.
Clinical Applications
Choose the needle that fits each patient and setting:
Pediatrics and Neonates
Tiny veins and sensitive skin make butterfly needles the best choice. Wings stabilize the needle and lower pain and anxiety.
Elderly or Frail Patients
Reduced subcutaneous tissue and fragile veins respond better to the gentle grip and flexible tubing of butterflies.
Chemotherapy and Critical Care
Patients need frequent draws. Butterfly needles cut trauma over multiple sticks. If you need large volumes (more than four 5 mL tubes), switch to a straight needle for speed.
Routine Health Checks
Straight needles speed up mass screenings and cut costs. Keep some butterfly sets on hand for hard-to-access veins.
Emergency and Intensive Care
Time is critical. Straight needles let you draw quickly for urgent labs. You can also use an indwelling catheter for repeated blood gases.
Procedure Steps and Best Practices
Preparation
- Confirm patient history, including allergies and blood-thinning medication.
- Keep the arm warm or use a tourniquet and gentle fist clenching to improve vein visibility.
Aseptic Technique and Needle Placement
- Follow CLSI GP41 guidelines for hand hygiene and glove use.
- For butterfly needles, tape the wings flat to the skin before inserting at a shallow angle (under 30°).
- For straight needles, stretch the skin taut and insert at a 30–45° angle.
First Tube and Order of Draw
- If you need a discard tube (for coagulation or flow cytometry), draw it first.
- Follow the recommended tube sequence to avoid additive interference: coagulation tubes first, then tubes without additives, and tubes with additives.
Controlling Flow and Mixing
- Keep draw speed around 2–4 mL per second. Faster flow can damage cells.
- Gently invert tubes 5–10 times right after filling to mix additives thoroughly.
Transport and Storage
- Send chemistry and immunology samples at room temperature or 4 °C within two hours.
- Handle blood gas samples immediately or place them on ice to prevent gas exchange.
Needle Removal and Disposal
- Remove the needle and apply pressure for 1–2 minutes, keeping the arm elevated.
- Discard needles and tubing in a certified sharps container to prevent injuries and contamination.
Final Thoughts
Butterfly and straight needles each bring clear benefits to blood collection. Butterfly needles reduce trauma and keep sample quality high, while straight needles speed up high-volume draws and cut costs. Lab teams should follow international guidelines (CLSI, ISO) to match needle choice with patient needs, test requirements, and workload. By fine-tuning supplies and processes, you can deliver safe, accurate, and patient-friendly blood collection for every clinical scenario.
For high-quality medical needles, visit Siny Medical today.
🔗 Follow us on YouTube for more medical insights: Siny Medical YouTube
🔗 Check out our manufacturing details here: Siny Medical on Made-in-China
FAQs
1. Can butterfly needles be reused?
No, they are single-use devices and must be discarded after one procedure.
2. Are butterfly needles safer?
Yes, especially for patients with fragile or hard-to-access veins. Their design minimizes trauma and improves first-stick success rates.
3. Do butterfly needles cost more?
Yes, but the increased comfort and lower sample rejection rates often justify the higher price.
4. Which is better for large volume blood draws?
Straight needles are better for drawing multiple large tubes quickly.
5. Where can I buy these needles online?
You can purchase both butterfly and straight needles directly from Siny Medical’s online store.